Booleans are a subclass of int
In Python, Booleans are a subclass of integers:
>>> isinstance(True, int)
True
>>> isinstance(False, int)I've known this for a long time, and this even allows you to write things like
>>> True + True # 1 + 1
2
>>> True * False # 1 * 0
0In fact, I tweeted about this recently.
What I didn't know is that True and 1 are equal,
much like False and 0 are equal:
In lots of programming languages 0 is False and 1 is True. For example if you say x = 0, and check if x == True it will return False, whereas if x = 1 it will return True.
— Matthew 🍵 (@uxai_net) February 8, 2022
Python just giving you some extra easter eggs to play with 😄
Isn't that interesting?
In hindsight, I shouldn't be so surprised... After all, Booleans can be converted to integers:
>>> int(True)
1
>>> int(False)
0and the Truthy and Falsy value of integers means that integers can also be converted to Booleans:
>>> bool(1)
True
>>> bool(0)
False
## And other integers (and floats) can be converted to `True`:
>>> bool(73)
True
>>> bool(0.5)
TrueSo, these two conversions, plus the fact that bool is a subclass of int
makes this fact a bit more understandable...
But still!
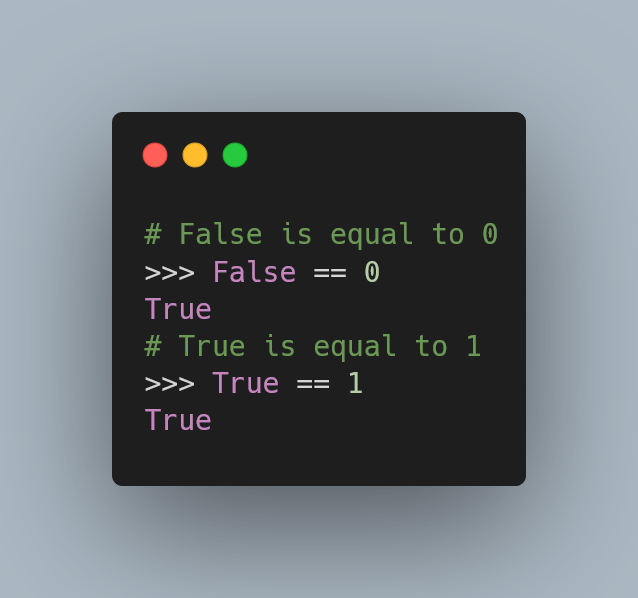
>>> True == 1
True
>>> False == 0
TrueAs to whether True and False being interpretable as integers is useful or not: it is.
When to use Booleans as integers in Python?
Booleans can be interpreted as integers, for example, to count objects that satisfy a given property, or to flatten some conditions.
I recorded a short YouTube video on the subject, that you can watch here.
In that video, I explain how we can use Booleans to count things; for example, the total amount of numbers in the list below that are divisible by 4:
nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
sum(not num % 4 for num in nums)That's it for now! Stay tuned and I'll see you around!
Become the smartest Python 🐍 developer in the room 🚀
Every Monday, you'll get a Python deep dive that unpacks a topic with analogies, diagrams, and code examples so you can write clearer, faster, and more idiomatic code.