How to draw a Bézier curve
Today I learned that there is a straightforward way to draw Bézier curves and I wrote a small Python program to test this out.
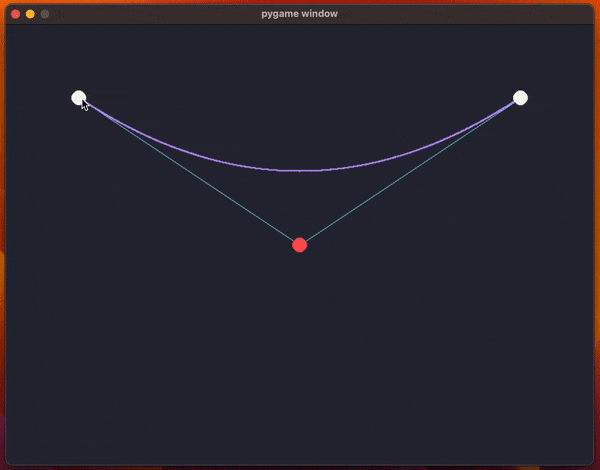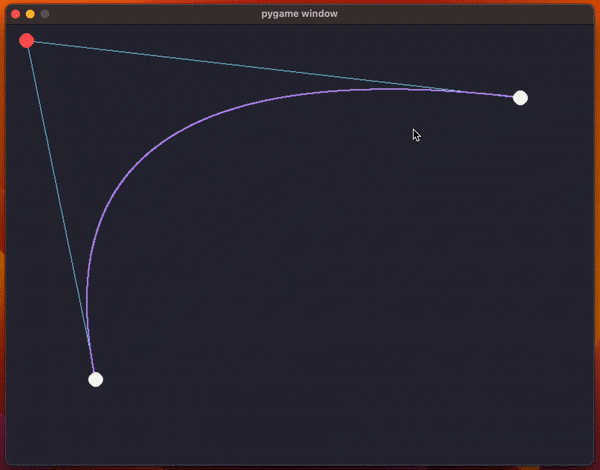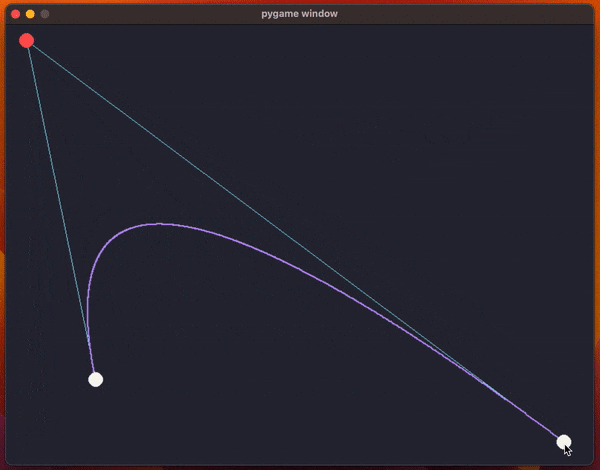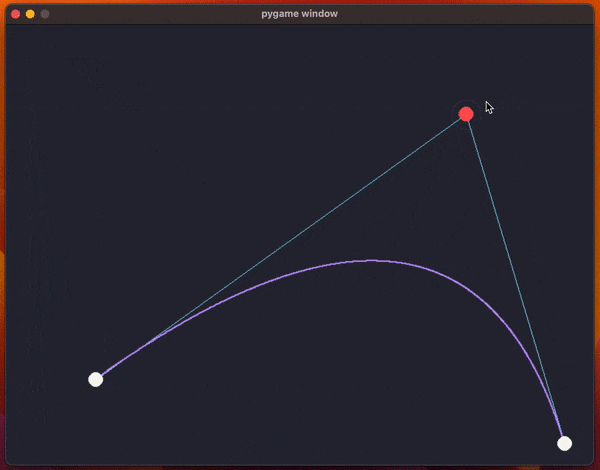
The code uses pygame and it creates a window with the two endpoints for the curve and a control point (so, we're drawing a quadratic Bézier curve).
The animation above shows the program running and the code has been included below.
The main part of that program is the little bit of maths that actually computes the points of the curve itself. For a given \(t \in [0, 1]\), if \(s\), \(e\), and \(c\) and the start, end, and control points, respectively, then the point \(p(t)\) of the curve is
\[ \begin{cases} p_1(t) = s + (c - s) \times t \\ p_2(t) = c + (e - c) \times t \\ p(t) = p_1(t) + (p_2(t) - p_1(t)) \times t \end{cases}\]
This formula is the application of the De Casteljau's algorithm to quadratic Bézier curves.
What the code does, inside the function draw_curve, is use a for loop to sample multiple values of t to approximate the curve by drawing a bunch of points.
The code below ran on Python 3.11 and pygame 2.5.1. It shouldn't have major compatibility issues with other version of Python/pygame, though, as I'm only using fairly basic functionality.
import dataclasses
from dataclasses import dataclass
import sys
import pygame
import pygame.locals
WIDTH = 800
HEIGHT = 600
ENDPOINT_COLOUR = (248, 248, 242)
BACKGROUND = (40, 42, 54)
CONTROL_POINT_COLOUR = (255, 85, 85)
CURVE_COLOUR = (189, 147, 249)
GUIDELINE_COLOUR = (139, 233, 253)
POINT_RADIUS = 10
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT))
screen.fill(BACKGROUND)
@dataclass
class Curve:
start: tuple[int, int]
end: tuple[int, int]
control_point: tuple[int, int]
def dist_squared(p1, p2):
x1, y1 = p1
x2, y2 = p2
return (x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2
def draw_endpoint(screen, point):
pygame.draw.circle(
screen,
ENDPOINT_COLOUR,
point,
radius=POINT_RADIUS,
)
def draw_control_point(screen, point):
pygame.draw.circle(
screen,
CONTROL_POINT_COLOUR,
point,
radius=POINT_RADIUS,
)
def draw_curve(screen, curve):
pygame.draw.line(screen, GUIDELINE_COLOUR, curve.start, curve.control_point)
pygame.draw.line(screen, GUIDELINE_COLOUR, curve.end, curve.control_point)
sx, sy = curve.start
ex, ey = curve.end
cx, cy = curve.control_point
iters = 1000
for iter in range(0, iters + 1):
delta = iter / iters
m1x = sx + (cx - sx) * delta
m2x = cx + (ex - cx) * delta
m1y = sy + (cy - sy) * delta
m2y = cy + (ey - cy) * delta
px = m1x + (m2x - m1x) * delta
py = m1y + (m2y - m1y) * delta
pygame.draw.circle(screen, CURVE_COLOUR, (px, py), radius=1)
draw_endpoint(screen, curve.start)
draw_endpoint(screen, curve.end)
draw_control_point(screen, curve.control_point)
previous_curve = None
curve = Curve((100, 100), (WIDTH - 100, 100), (WIDTH // 2, HEIGHT // 2))
dragging = False
point_being_dragged = None
print("Click a point to “pick it up” and click again to drop it.")
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if (
event.type == pygame.locals.QUIT
or event.type == pygame.locals.KEYDOWN
and event.key == pygame.locals.K_q
):
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
# Are we starting/stopping to drag something?
elif (
event.type == pygame.locals.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN
and event.button == pygame.locals.BUTTON_LEFT
):
if not dragging:
pos = event.pos
if dist_squared(pos, curve.start) <= POINT_RADIUS**2:
point_being_dragged = "start"
elif dist_squared(pos, curve.end) <= POINT_RADIUS**2:
point_being_dragged = "end"
elif dist_squared(pos, curve.control_point) <= POINT_RADIUS**2:
point_being_dragged = "control_point"
if point_being_dragged is not None:
dragging = True
else:
dragging = False
point_being_dragged = None
# Are we dragging a point?
elif dragging and event.type == pygame.locals.MOUSEMOTION:
setattr(curve, point_being_dragged, event.pos)
if previous_curve != curve:
screen.fill(BACKGROUND)
draw_curve(screen, curve)
previous_curve = dataclasses.replace(curve)
pygame.display.flip()
Become the smartest Python 🐍 developer in the room 🚀
Every Monday, you'll get a Python deep dive that unpacks a topic with analogies, diagrams, and code examples so you can write clearer, faster, and more idiomatic code.
References
- https://blog.richardekwonye.com/bezier-curves [last accessed 04-09-2023]