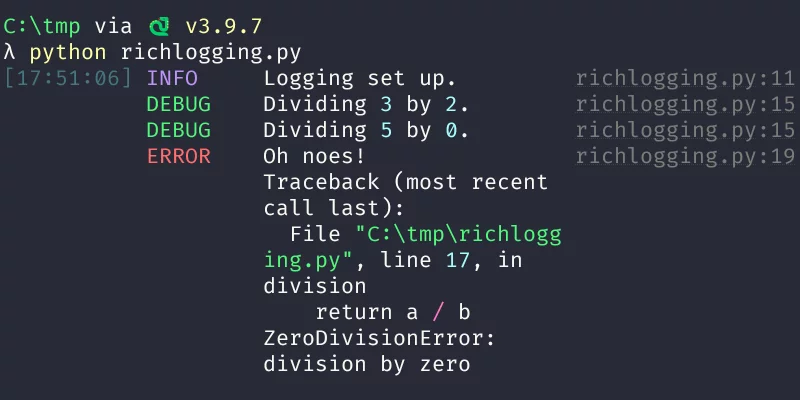
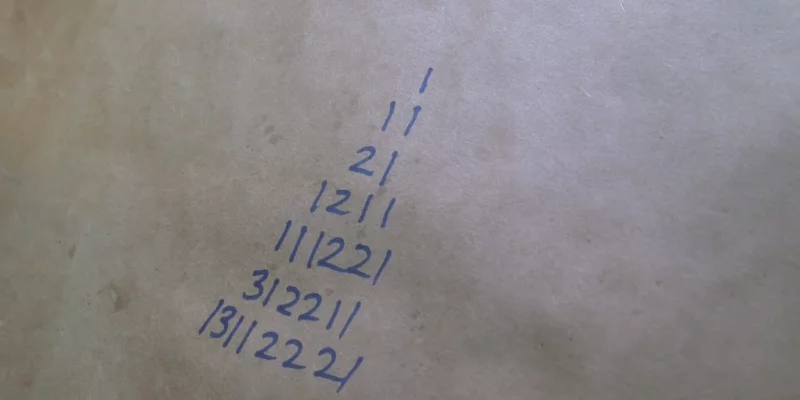Today I learned how you can do beautiful console logging by using the module rich.
This is the story of how I started contributing to open source and, in particular, how I tackled issue #2073 of the well-known Python library rich, by Will McGugan.
Let me show you characteristics of APL that will influence your understanding of programming concepts and the way you use other languages.
We discuss the look-and-say sequence, its behaviour, variations of it, and a Python implementation.
Today I learned how to use the function pandas.show_versions to get system diagnostic information.
Today I learned how to run the black Python code formatter as a pre-commit hook on git.
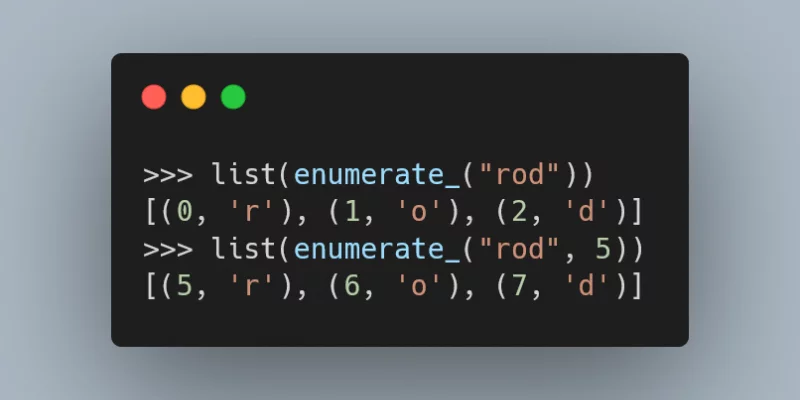
In this article we reimplement the built-in enumerate in the best way possible.
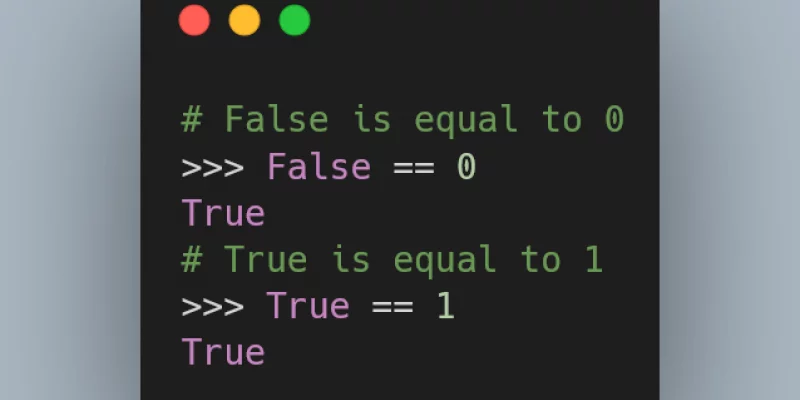
The Zen of Python says “there should be one -- and preferably only one -- obvious way to do it”, but what if there's a dozen obvious ways to do it?
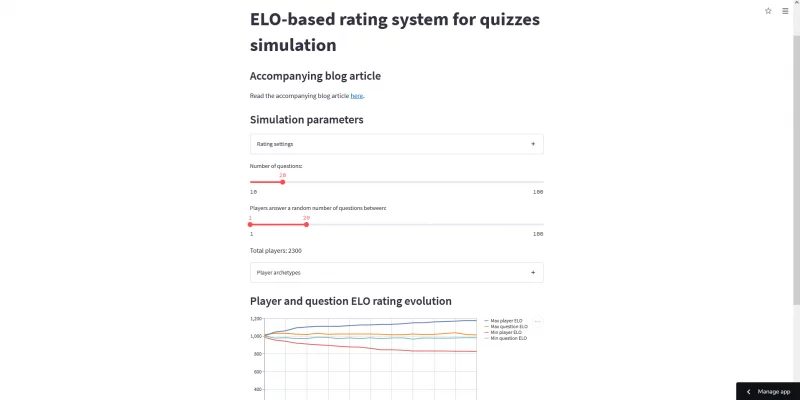
Join me as I create a simulation that tries to test an Elo-based rating system for quizzes.
Today I learned that you can build web apps with Python using streamlit.
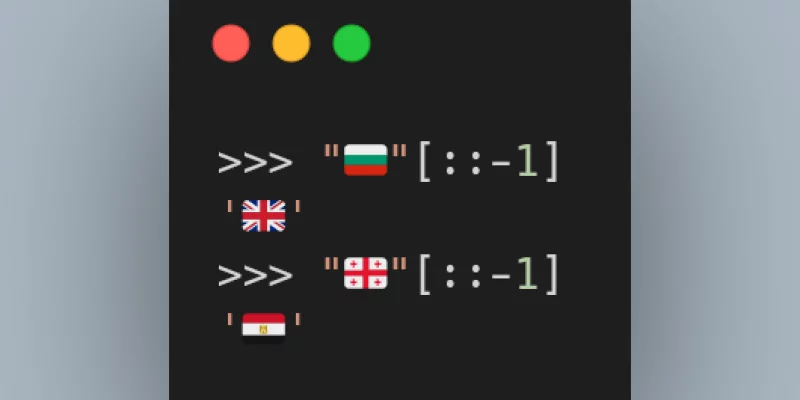
Today I learned that the reverse of some flag emoji are other flags!
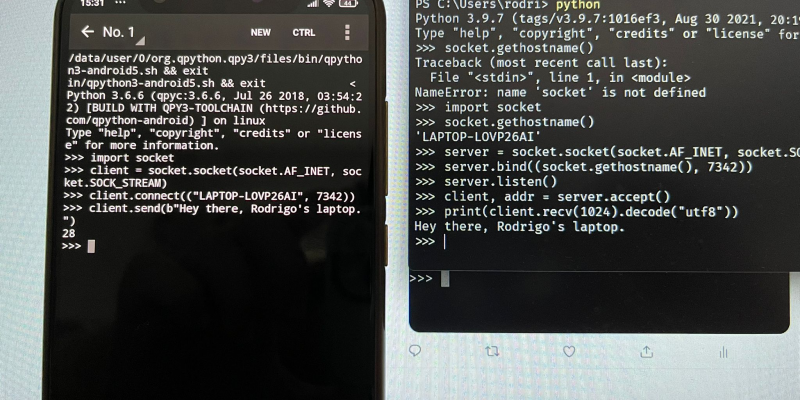
Create a simple chatroom server in Python by following along this tutorial series.
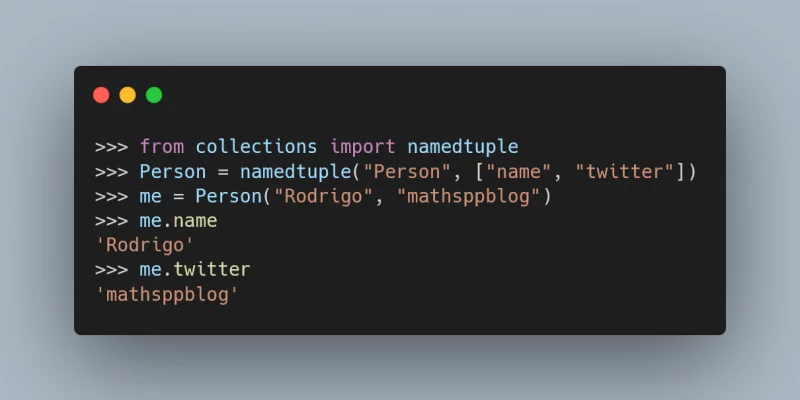
Today I learned how to use the namedtuple from the module collections.
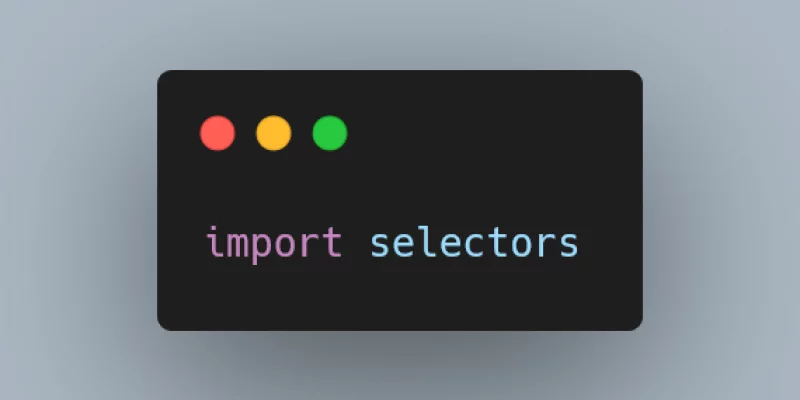
Today I learned about the Python module selectors to manage multiple socket connections.
Dive into the world of socket programming with this Python tutorial that assumes 0 prior experience.